Page 20 - ILK Research Report 2020
P. 20
Doctorate Dr.-Ing. Maximilian Schadhauser
Injection Molding with Continuous Fibre Feed –
Method, Model Design and Model Validation
Supervising Professor: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Niels Modler
Driven by cost pressures of international markets and an fibres are directly fed into an injection-molding plasticizing
upcoming urge to preserve limited resources, an increas- unit. Due to this configuration, a preprocessing step uti-
ing demand can be observed regarding new cost-efficient lizing, e. g., a twin-screw extruder is no longer necessary.
and sustainable methods for manufacturing long-fibre-re- However, directly feeding continuous fibres into an injec-
inforced thermoplastic parts. Such cost-efficient and tion-molding plasticizing unit goes along with difficulties
sustainable methods may relate to the concept of di- regarding, i. a., fibre impregnation, fibre length structure
rect-processing, which is characterized in that the formerly and fibre-melt homogenization. To overcome these diffi-
separate steps of compounding and molding are merged culties, a variety of new measures and components has
into one single processing step. As a result, a reduction of been introduced.
process-related costs and CO2 emissions may be achieved.
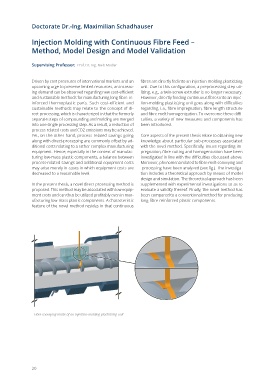
Yet, on the other hand, process-related savings going Core aspects of the present thesis relate to obtaining new
along with direct-processing are commonly offset by ad- knowledge about particular sub-processes associated
ditional costs relating to a rather complex manufacturing with the novel method. Specifically, issues regarding im-
equipment. Hence, especially in the context of manufac- pregnation, fibre cutting and homogenization have been
turing low-mass plastic components, a balance between investigated in line with the difficulties discussed above.
process-related savings and additional equipment costs Moreover, phenomena related to fibre-melt-conveying and
may arise merely in cases in which equipment costs are -processing have been analyzed (see fig.). The investiga-
decreased to a reasonable level. tion includes a theoretical approach by means of model
design and simulation. The theoretical approach has been
In the present thesis, a novel direct-processing method is supplemented with experimental investigations so as to
proposed. This method may be associated with low equip- evaluate a validity thereof. Finally, the novel method has
ment costs and can thus be utilized profitably even in man- been compared to a conventional method for producing
ufacturing low-mass plastic components. A characteristic long-fibre-reinforced plastic components.
feature of the novel method resides in that continuous
Fibre conveying inside of an injection-molding plasticizing unit
20