Page 44 - SaxoCell Annual Report22/23
P. 44
This work is currently under review at Frontiers in Immunology. For potential use as a release-
relevant assay, the proliferation assay was transferred to cell lines for better validation.
To improve quality control of cell-based drugs, such as Palintra®, a functional software
demonstrator "AI Flow Software Algorithm" was developed for automated analysis of flow
cytometric measurements, a publication on this has been submitted.
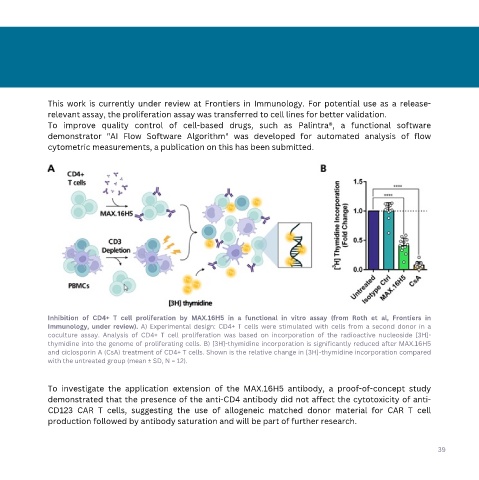
Inhibition of CD4+ T cell proliferation by MAX.16H5 in a functional in vitro assay (from Roth et al, Frontiers in
Immunology, under review). A) Experimental design: CD4+ T cells were stimulated with cells from a second donor in a
coculture assay. Analysis of CD4+ T cell proliferation was based on incorporation of the radioactive nucleoside [3H]-
thymidine into the genome of proliferating cells. B) [3H]-thymidine incorporation is significantly reduced after MAX.16H5
and ciclosporin A (CsA) treatment of CD4+ T cells. Shown is the relative change in [3H]-thymidine incorporation compared
with the untreated group (mean ± SD, N = 12).
To investigate the application extension of the MAX.16H5 antibody, a proof-of-concept study
demonstrated that the presence of the anti-CD4 antibody did not affect the cytotoxicity of anti-
CD123 CAR T cells, suggesting the use of allogeneic matched donor material for CAR T cell
production followed by antibody saturation and will be part of further research.
39